Automated Smart Management Workshop: CentOS/RHEL migration and upgrade
Read this in other languages:
 English,
English,  Français.
Français.
Introduction
This use-case will focus on conversion from CentOS (though this could be another RHEL derivitive) to RHEL while maintaining a 3 tier application stack (do no harm). While we only show this process for a few systems, it can be scaled to a larger number of physical, virtual or cloud hosts using content repos provided by Red Hat Satellite (included in Red Hat Smart Management). The conversion process will be driven with automation built and run using Ansible Automation Platform.
Environment
- Satellite 6.x, Ansible Automation Platform 4.x
- 3x CentOS 7 instances
- 3x RHEL 7 instances
Exercise Scenario
- Exercise: Convert CentOS 7 to RHEL 7
Overview
Summary
- Remember, during initial environment setup, we created a backup of the instance data (in case a fallback or restore is needed. Better safe than sorry.)
- We will utilize an additional project in Ansible Automation Platform, “Three Tier App / Dev”, which will allow us to install (take a guess) a three tier application stack across the three CentOS nodes. Additionally, the project also provides a means to test/verify functionality of the application components, which we will perform pre RHEL conversion.
- Next, we employ the Convert2RHEL utility to convert the CentOS nodes to RHEL. There are many sources of information on this handy utility, here are several of note:
- Verify functionality of the application stack post RHEL conversion.
Things to consider if doing this in dev/test/stage-beta/prod:
- Commercial and/or in-house developed application version(s) support with the host OS
- Bootloader changes
- Network connection and network time synchonizations
| A Note about using Satellite vs. Ansible Automation Platform for this… |
|---|
| Out of the box, Satellite 6 supports RHEL systems roles (a collection of Ansible Roles) for a limited set of administration tasks. Satellite can be used to do OS conversions and upgrades, however an Ansible Automation Platform Subscription is required to execute complicated OS conversions and upgrades that require logic to meet up-time requirements. Using these two solutions together ensures you have the best tool for the job for: - Content Management (Satellite) - OS Patching & Standardized Operating Environments (Satellite) - Provisioning: OS, Infra Services and Applications/Other (Satellite and/or Ansible Automation Platform) - Configuration of Infra and Apps (Ansible Automation Platform) Reference: Converting CentOS to RHEL with Red Hat Satellite 6 and Leapp Upgrade with Satellite 6 |
Ok, let’s get started…
Pre-requisites
-
Exercise 0: Lab Setup
-
Organization to be used = Default Organization
-
Location to be used = Default Location
-
A content view = RHEL7
-
Lifecycle environments = Dev, QA, Prod
Exercise:
Login to your Satellite & AAP UI’s
NOTE The following are example URLs. Your student lab URLs will be different.
- Ansible Automation Platform URL
Example: https://student1.{random}.example.opentlc.com*- Satellite URL
Example: https://student1-sat.{random}.example.opentlc.com (Note the -sat added to the URL)*
Note that in the following steps that are being performed on AAP, at any time, over on the Satellite console, review the registered hosts via clicking Hosts => All Hosts. Refresh the Hosts page to see changes as they occur a result from the automation being performed via AAP.
Steps:
1. Logging into the Ansible Automation Platform (AAP)
- Use a web browser on your computer to access the AAP GUI via the link found in the Environment above. And use the following username and password to login: *admin /
*

- Upon successful login, you will be able to see the Ansible Automation Platform dashboard.
2. Install Three Tier Application Stack
-
Use the side pane menu on the left to select Templates.
-
Click
 to the right of CONVERT2RHEL / 96 - Three Tier App deployment to launch the job. This will take ~2 minutes to complete.
to the right of CONVERT2RHEL / 96 - Three Tier App deployment to launch the job. This will take ~2 minutes to complete.
3. Take CentOS node snapshot (optional, however, recommended for this exercise)
-
Use the side pane menu on the left to select Templates.
-
Click
 to the right of CONVERT2RHEL / 01 - Take node snapshot to copy the template.
to the right of CONVERT2RHEL / 01 - Take node snapshot to copy the template.
-
Click the newly created job template CONVERT2RHEL / 01 - Take node snapshot @ some-timestamp
-
Click Edit at the bottom left.
- Edit the name to CONVERT2RHEL / 01 - Take node snapshot / CentOS7 Development
- In the Variables section, within tags remove:
“short_name”: “node*”,
…and add:
“ContentView”: “CentOS7”,
“Environment”: “Dev”,
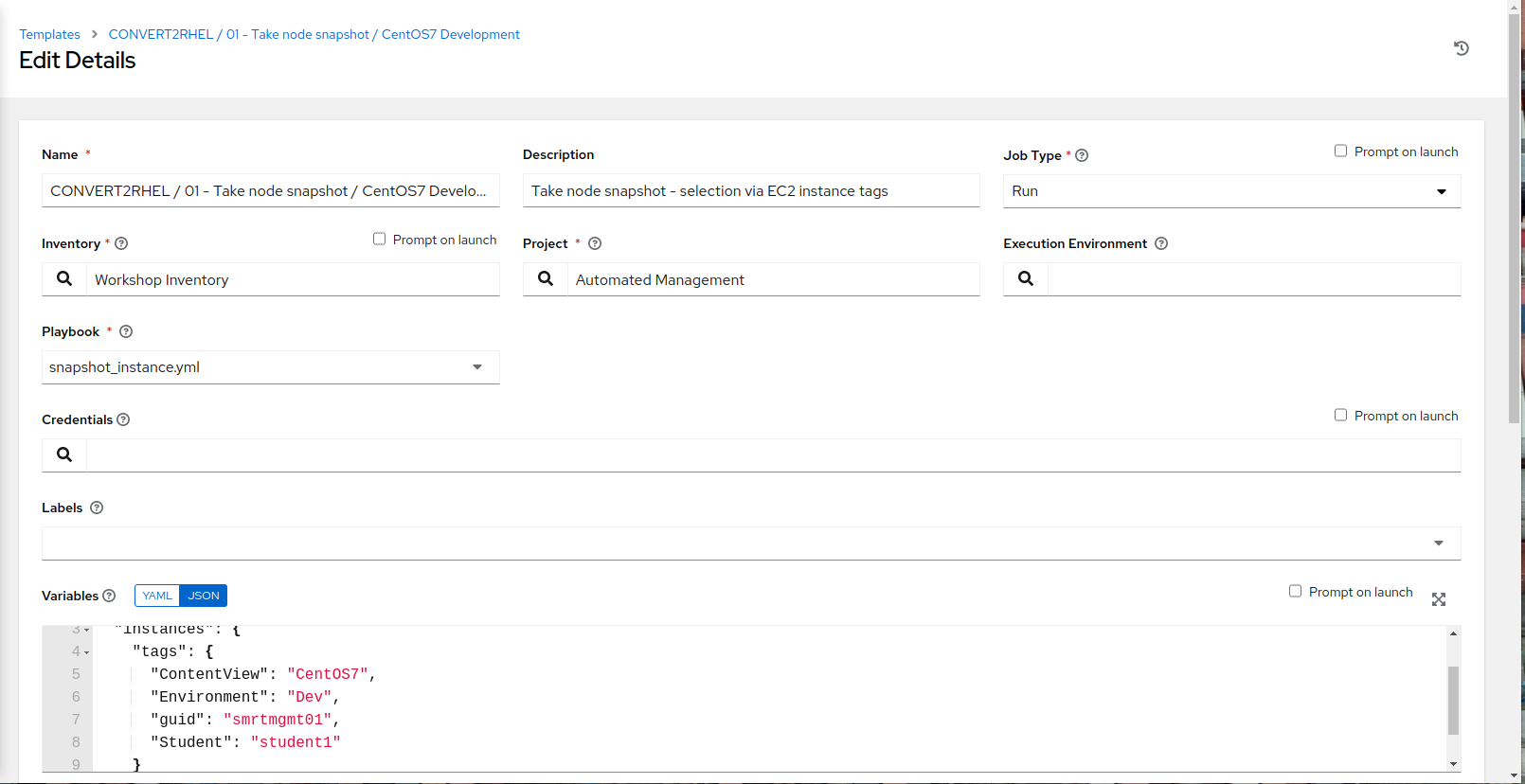
- Review the changes, then at the bottom left, click Save
- Verify the template name change, as well as the tag adjustments in the Variables section then click Launch
- Selecting launch will take you to the Jobs > CONVERT2RHEL / 01 - Take node snapshot / CentOS7 Development output window where you will be able to follow each task executed as part of the playbook. This will take approximately 5 mins to complete.
4. Verify three tier application functionality on CentOS nodes - pre Centos update
-
Use the side pane menu on the left to select Templates.
- Click
 to the right of CONVERT2RHEL / 97 - Three Tier App smoke test to launch the job.
to the right of CONVERT2RHEL / 97 - Three Tier App smoke test to launch the job. - Selecting launch will take you to the Jobs > CONVERT2RHEL / 97 - Three Tier App smoke test output window where you will be able to follow each task executed as part of the playbook. This will take approximately 30 secs to complete.
5. Upgrade CentOS nodes to latest version
-
Use the side pane menu on the left to select Templates.
-
Click
 to the right of CONVERT2RHEL / 02 - Upgrade OS to latest release to launch the job.
to the right of CONVERT2RHEL / 02 - Upgrade OS to latest release to launch the job. -
Selecting launch will take you to the Jobs > CONVERT2RHEL / 02 - Upgrade OS to latest release output window where you will be able to follow each task executed as part of the playbook. This will take approximately 6 mins to complete.
6. Verify three tier application functionality on CentOS nodes - post Centos update, pre Convert2RHEL
-
Use the side pane menu on the left to select Templates.
-
Click
 to the right of CONVERT2RHEL / 97 - Three Tier App smoke test to launch the job.
to the right of CONVERT2RHEL / 97 - Three Tier App smoke test to launch the job. -
Selecting launch will take you to the Jobs > CONVERT2RHEL / 97 - Three Tier App smoke test output window. This will take approximately 30 secs to complete.
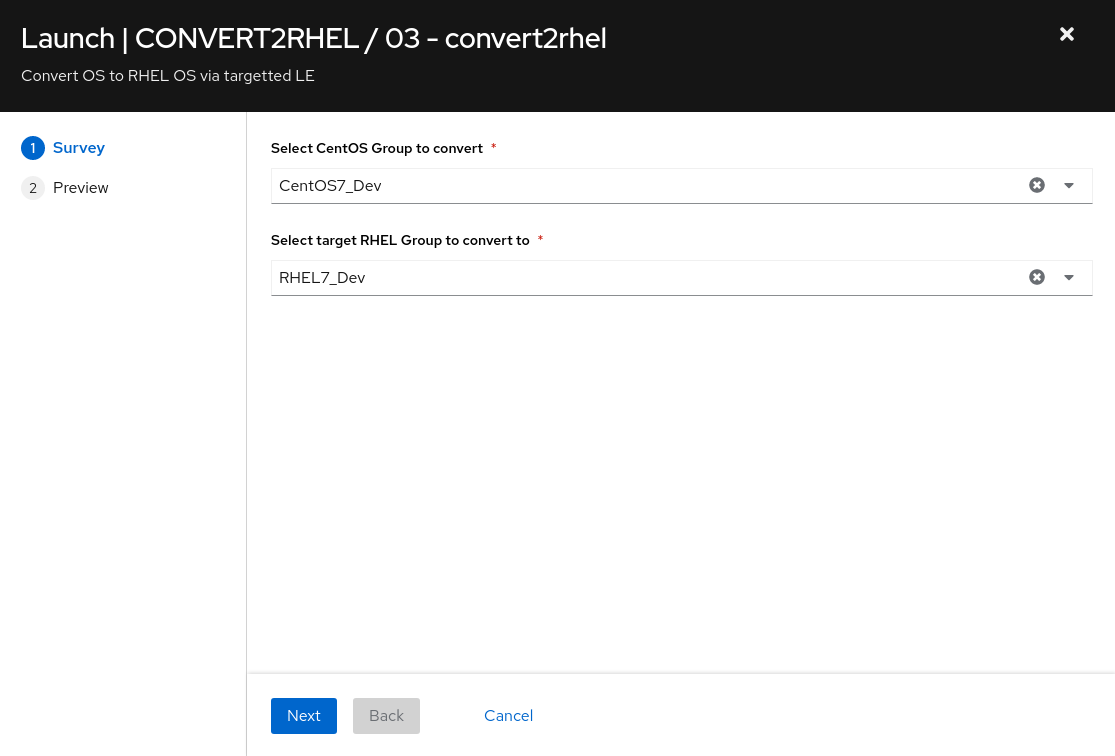
7. Convert2RHEL - CentOS7 Development nodes to RHEL7 Development nodes
-
Use the side pane menu on the left to select Templates.
-
Click
 to the right of CONVERT2RHEL / 03 - convert2rhel to launch the job.
to the right of CONVERT2RHEL / 03 - convert2rhel to launch the job.- choose LE group to convert CentOS7_Dev
- choose LE target RHEL7_Dev
-
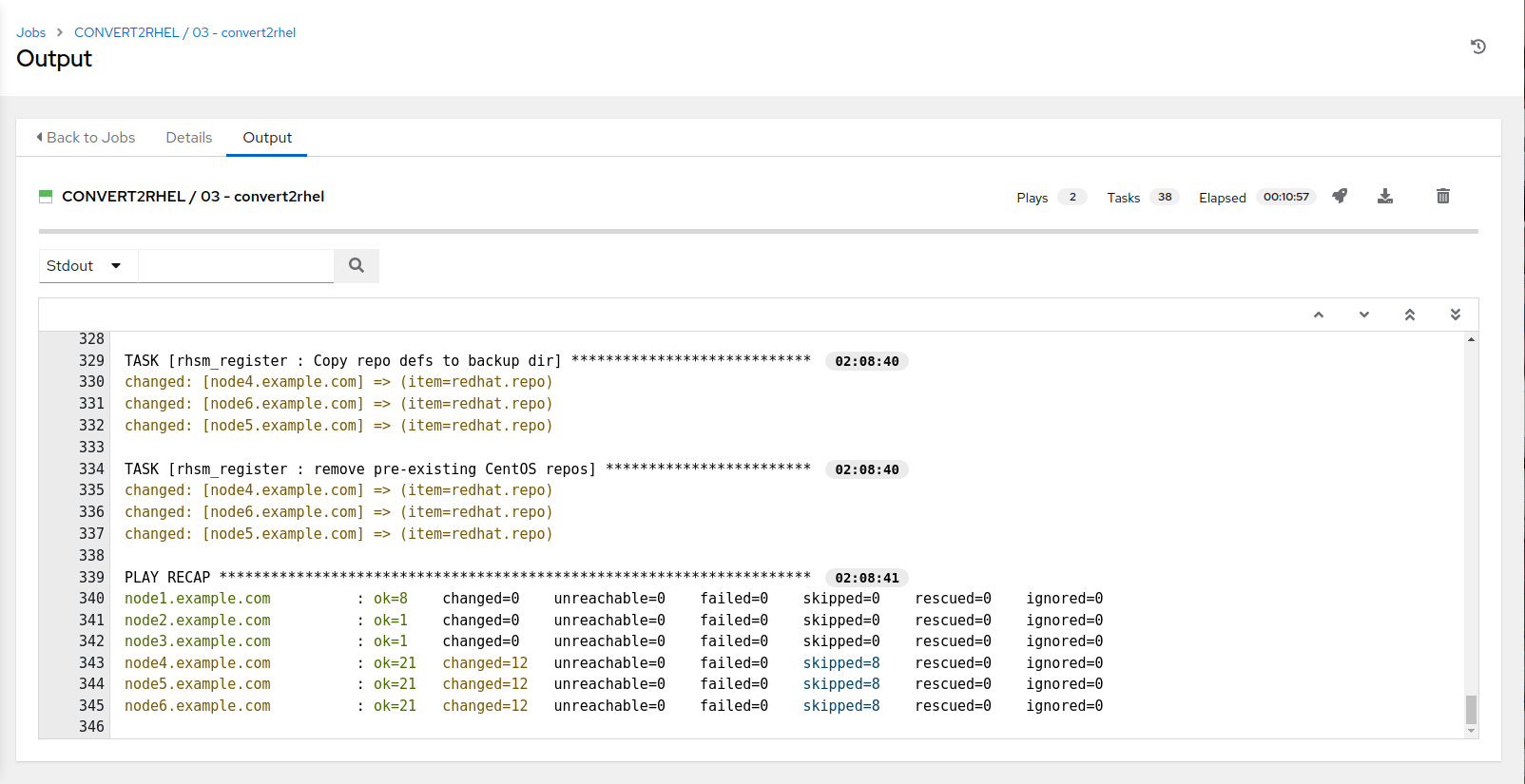
Selecting launch will take you to the Jobs > CONVERT2RHEL / 03 - convert2rhel output window. This will take approximately 11 mins to complete.
NOTE with some pre-configuration, any combination is possible
- click Next to continue
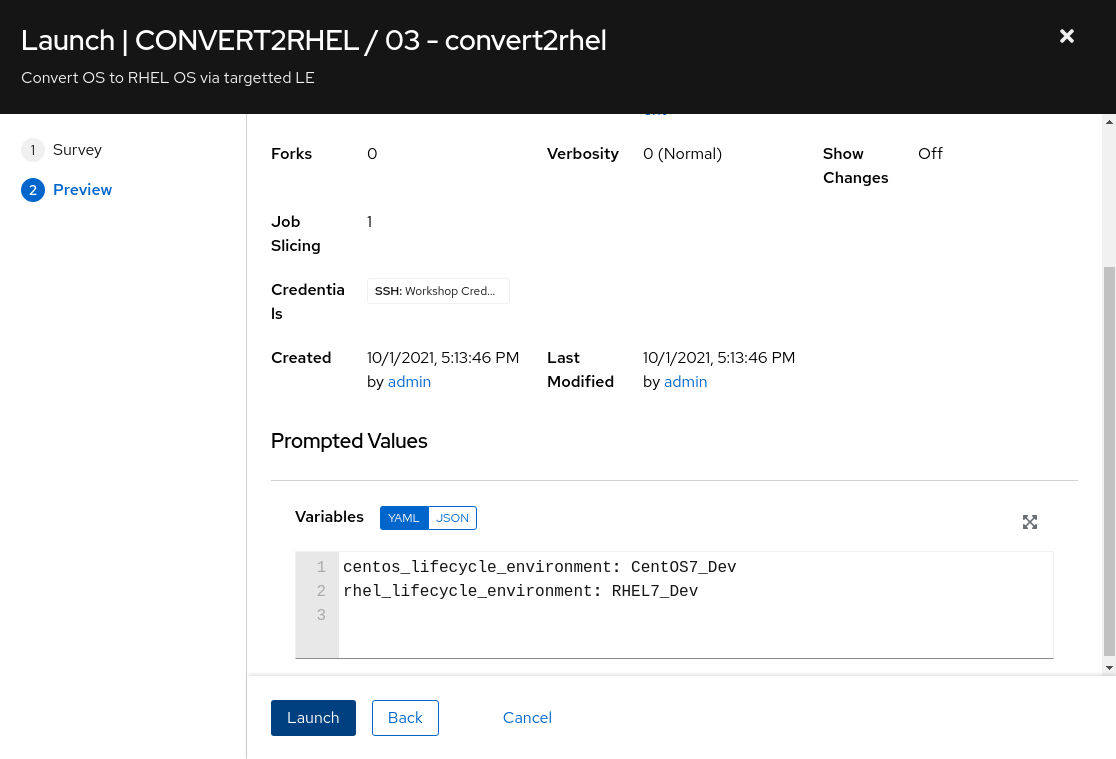
- confirm CentOS and RHEL LE variables set via survey selections and click Launch
If you look in Satellite now (Hosts > All Hosts), you will see that all CentOS notes have been converted to RHEL 7.9 nodes.
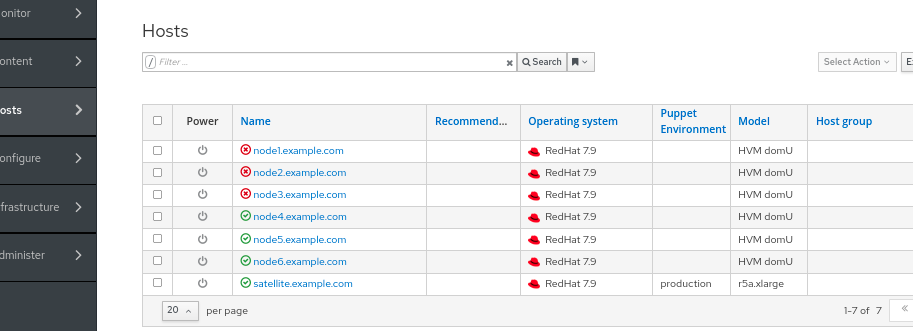
8. Query Satellite to get post conversion node-related details, set EC2 instance tags based on these details
-
Use the side pane menu on the left to select Templates.
-
Click
 to the right of EC2 / Set instance tags based on Satellite(Foreman) facts to launch the job.
to the right of EC2 / Set instance tags based on Satellite(Foreman) facts to launch the job.
-
Selecting launch will take you to the Jobs > EC2 / Set instance tags based on Satellite(Foreman) facts output window. This will take approximately 30 secs to complete.
9. Update inventories via dynamic sources
-
Use the side pane menu on the left to select Templates.
- Click
 to the right of CONTROLLER / Update inventories via dynamic sources to launch the job.
to the right of CONTROLLER / Update inventories via dynamic sources to launch the job.
- Select “CentOS7” for Inventory To Update
- Select “Dev” for Choose Environment
- Click Next, confirm prompted values, then click Launch
- Selecting launch will take you to the Jobs > CONTROLLER / Update inventories via dynamic sources output window. This will take approximately 30 secs to complete.
-
Use the side pane menu on the left to select Templates.
- Click
 to the right of CONTROLLER / Update inventories via dynamic sources to launch the job.
to the right of CONTROLLER / Update inventories via dynamic sources to launch the job.
- template CONTROLLER / Update inventories via dynamic sources
- Select “RHEL7” for Inventory To Update
- select “Dev” for Choose Environment
- Click Next, confirm prompted values, then click Launch
-
Selecting launch will take you to the Jobs > CONTROLLER / Update inventories via dynamic sources output window. This will take approximately 30 secs to complete.
- If you look in Inventories > RHEL7 Development you will now see that nodes[1-6] are in the inventory.
10. Create a converted RHEL credential
- Use the side pane menu on the left to select Credentials.
- Click
 to the right of Workshop Credential to copy the credential.
to the right of Workshop Credential to copy the credential.
-
Click the newly created credential Workshop Credential @ some-timestamp
-
Click Edit at the bottom left.
- Edit the name to Converted RHEL Credential
- Change the username from “ec2-user” to “centos”
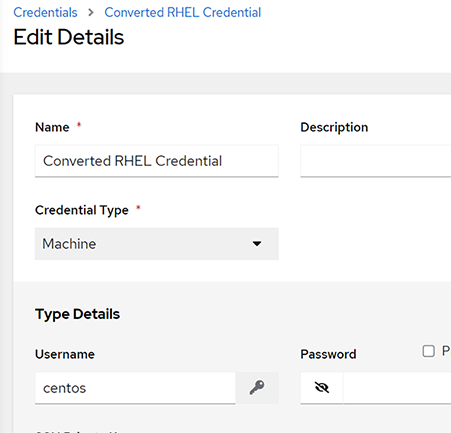
- Click Save
11. Copy template CONVERT2RHEL / 97 - Three Tier App smoke test to template CONVERT2RHEL / 97 - Three Tier App smoke test / RHEL7 Development
-
Use the side pane menu on the left to select Templates.
-
Click
 to the right of CONVERT2RHEL / 97 - Three Tier App smoke test to copy the template.
to the right of CONVERT2RHEL / 97 - Three Tier App smoke test to copy the template.
-
Click the newly created job template CONVERT2RHEL / 97 - Three Tier App smoke test @ some-timestamp
-
Click Edit at the bottom left.
- Edit the name to CONVERT2RHEL / 97 - Three Tier App smoke test / RHEL7 Development
- Click
 under Inventory and select the radio button for RHEL7 Development, followed by Select.
under Inventory and select the radio button for RHEL7 Development, followed by Select. - Click
 under Credentials and select the radio button for Converted RHEL Credential, followed by Select.
under Credentials and select the radio button for Converted RHEL Credential, followed by Select. - Review the changes, then scroll down and on the bottom left, click Save
- Click Launch to run the new job template CONVERT2RHEL / 97 - Three Tier App smoke test / RHEL7 Development
- Selecting launch will take you to the Jobs > CONVERT2RHEL / 97 - Three Tier App smoke test / RHEL7 Development output window. This will take approximately 30 secs to complete.
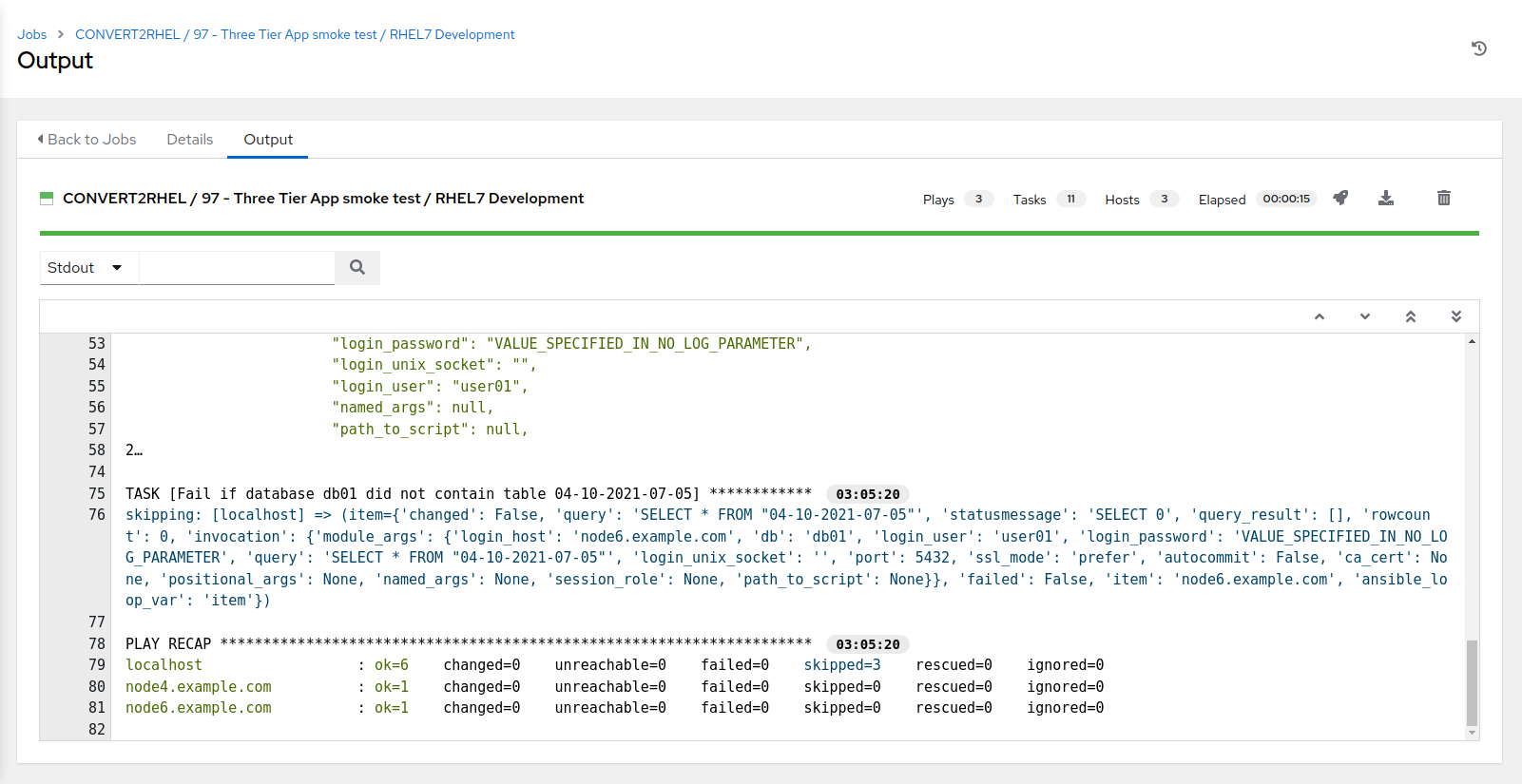
The Three Tier App smoke test template should have completed successfully, which shows that we were able to complete the migration from CentOS 7 to RHEL 7, and when that process finished, our 3 tier application still functioned.
EXTRA CREDIT - Convert2RHEL workflow template Create a workflow template incorporating the above standalone templates into a complete CentOS to RHEL conversion workflow!
EXTRA CREDIT - Infrastructure-as-Code “Choose Your Own Adventure”
- Fork Automated Smart Management repo to individual GitHub account Before we begin, you’ll need to fork the Automated Smart Management repo into your personal GitHub account. If you do not have an individual GitHub account, you will need to create one to proceed. Utilization of a source code management (SCM) system is central to the “infrastructure as code” concepts put forth in this lab exercise, and in this case, GitHub is our SCM.
Once logged into GitHub navigate to the Red Hat Partner Tech repo for Automated Smart Management repo. Next, on the Automated Smart Management repo page, in the top, upper right of the page, click “Fork”. This will create a “forked” Automated Smart Management repo in your personal GitHub account.
Switch the “Automated Management” project in AAP to utilize your newly cloned repo. The following files are some good places to start looking to see where you can adjust the Extra Vars instance tags to select/filter what particular instances that a job template/playbook gets run against:
group_vars/control/inventories.yml
group_vars/control/job_templates.yml
Once the updates are made, commit and push these changes to the cloned repo, followed by running the “SETUP / Controller” job template, which will propogate the changes to AAP itself. …